Database Systems Lecture 1
前言
首先,先祝各位新年快樂。
由於舊的電腦壞掉了,之前的文章都無了,加上新學期開了,打算重新開個新坑,希望這次我能堅持久點hhh。
介紹數據庫系統(Introduction to DB systems)
DB在我們的生活裡無處不在,甚至毫不誇張的說,DB是我們生活的一部分。
例如
- 銀行
- 外賣
- 網上購物
- 線上預約
動機(Motivations)
DB的開發動機主要作為以下目的,以及解決傳統的文件處理系統的不足之處:
文件處理系統(File-processing Systems)
- 持久的儲存並記錄在各種文件中(permanent records stored in various files)
- 為提取和添加記錄而編寫的應用程序 (application programs written to extract & add records)
傳統文件處理系統的缺點(Disadvantages of traditional file-processing systems)
- 數據冗餘&不一致(data redundancy & inconsistency)
- 數據訪問困難 (difficulty in accessing data)
- 數據隔離&不同數據格式 (data isolation & different data formats)
- 並發訪問異常 (concurrent access anomalies)
- 安全問題 (security problem)
- 完整性問題 (integrity problem)
什麼是DB?(What is a Database?)
DB 是一個非冗餘(non-redundant)且持久(persistent)的邏輯相關(logically-related)的記錄文件集合,該集合是結構化的,並且支持各種處理和檢索需求。
數據庫管理系統(Database Management System)
- 一組用於創建、存儲、更新和訪問數據庫數據的軟件程序。
通俗來說就是用來 增刪改查(CRUD)數據的數據軟件
- Create
- Read
- Update
- Delete
例子有
Oracle,MySQL和Oceanbase用於管理終端用戶和數據庫之間的交互
DBMS 與其他編程系統的分別(Difference between DBMS & other programming systems)
- 管理持久數據的能力(the ability to manage persistent data)
- 提供一個方便、高效、健壯的環境,用於檢索和存儲數據(to provide an environment that is convenient, efficient, and robust to use in retrieving and storing data)
其他數據庫管理系統功能 (Other DBMS capabilities)
- 數據建模 (data modeling)
- 用於定義、訪問和操作數據的高級語言 (high-level languages to define, access and manipulate data)
- 事務管理&並發控制 (transaction management & concurrency control)
- 訪問控制 (access control)
- 恢復 (recovery)
數據庫系統 (Database System)
- 硬件(Hardware)
- 軟件(Software)
- 操作系統(OS)
- 數據庫管理系統(DBMS)
- 應用(Application)
- 人員(People)
- 程序(Procedures)
- 數據(Data)
- 這是個硬件、軟件、人員、程序和數據的集成系統
- 定義和規範數據庫環境中數據的收集、存儲、管理和使用
數據庫系統架構 (DB System Architecture)
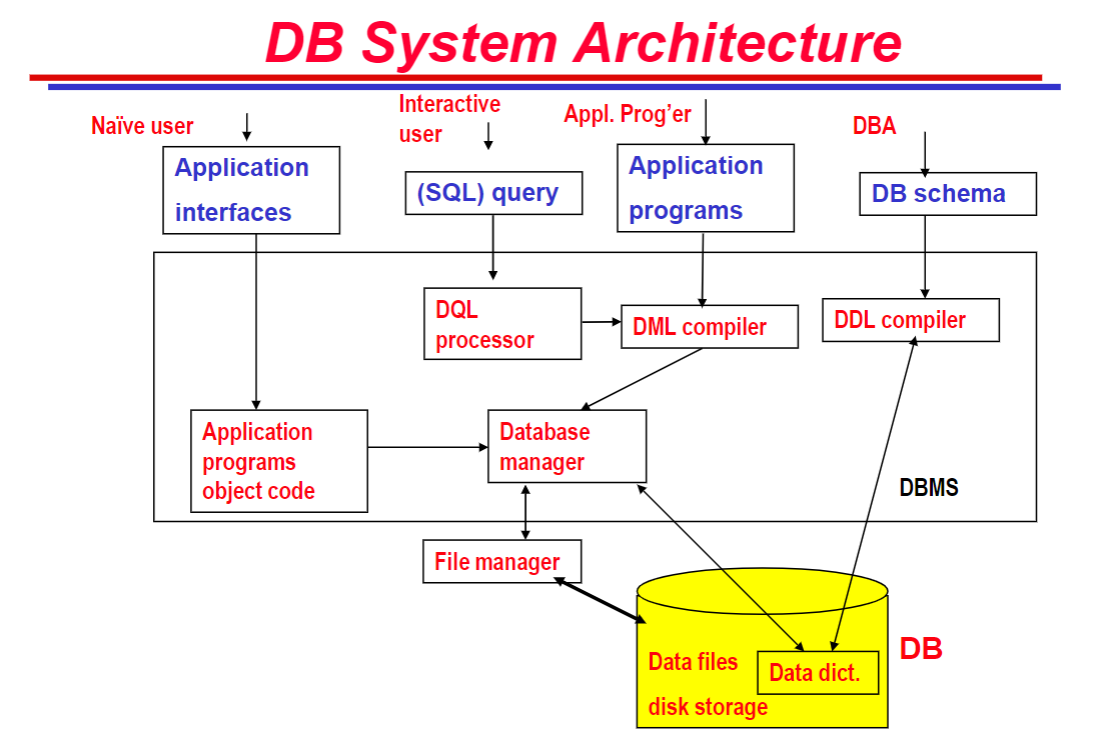
數據庫用戶
- Naive Users: Running application programs
- Interactive Users: Using query languages
- Application Programmers: Writing embedded DML in a host language
數據庫管理員 (DBA)
- DBA is the person who has central control over the DB
- Main functions of DBA:
- schema definition
- storage structure and access method definition
- schema and physical organization modification
- granting of authorization for data access
- integrity constraint specification
數據查詢語言 (DQL)
- a language used to make queries in databases
- e.g. search records with giving conditions (sex=“Female”)
數據操作語言 (DML)
- a language that enables users to manipulate data
- e.g. insert or delete records
數據定義語言 (DDL)
(Deadline DDL)- a language for defining DB schema
- e.g. create, modify, and remove database objects such as table, indexs, and users.
三層架構
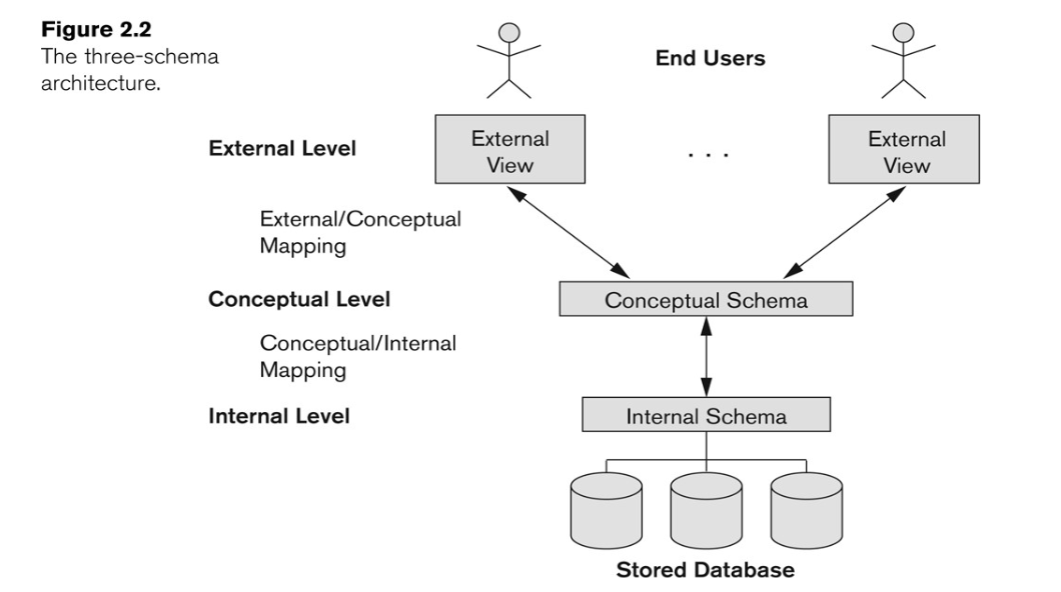
數據抽象 (Data Abstraction)
Data Abstraction
Abstract view of the data
- simplify interaction with the system
- hide details of how data is stored and manipulated
Levels of abstraction
- Physical/internal level: internal schema uses a physical data model and describes the complete details of data storage and access paths for the database.
- Conceptual level: conceptual schema describes the structure of the whole database for a community of users and hides the details of physical storage structures.
- View/external level: external schema describes the part of the database that a particular user group is interested in and hides the rest from that group.
Data Independence
the ability to modify a schema definition in one level without affecting a schema in the next higher
there r two kinds:
- physcial data independence:
– the ability to modify the physical schema without altering the conceptual schema and thus, without causing the application programs to be written
- logical data independence:
– the ability to modify the conceptual schema without casuing the application programs to be rewritten
Data Models
Data Models (Conceptual level)
- A collection of conceptual tools for describing data, data relationships, operations, and consistency constraints
- the “core” of database

The Entity-Relationship Model
Preliminaries
- Proposed by P.Chen in 1976
- Direct, easy-to-understand graphical notion
- Translate readily to relatinonal schema for database design

Three basic concept
Entity, Attribute, Relationship
Entity Model Concepts
Entity
- a distinguishable object with independent existence
Example: Jack Ma, CityU, HSBC…
Entity Set
- a set of entites of the smae type
Example: Student, Employee, University, Bank…
Attribute – information of entity
Example: Name, ID, Address, Sex are attributes of a studnet entity
Each attribute can take a value from a domain
Example: Name belong to Character String, ID belong to Integer, …
Formally, an attribute A is a function which maps from an entity set E into a domain D:
Type of Attributes
Simple
- Each entity has a single atomic value for the attribute. For example, SSN or Sex, name…
Composite
- The attribute maybe comosed of serveral components. For example:
- Address(Flat, Block, Street, City, State, Country)
- Composition may from a hierarchy where some components are themselves composite
Multi-valued
- An entity may have multiple values for that attribute. For example, Color of a CAR or PreviousDegrees of a STUDENT
- Denoted as {color} or {PreviousDegree}
- E.g. “{BSc, 1990}, {BMc, 1993}, {PhD, 1998}”
Example of a composite attribute
